Ethernet based Network Types found in OT networks

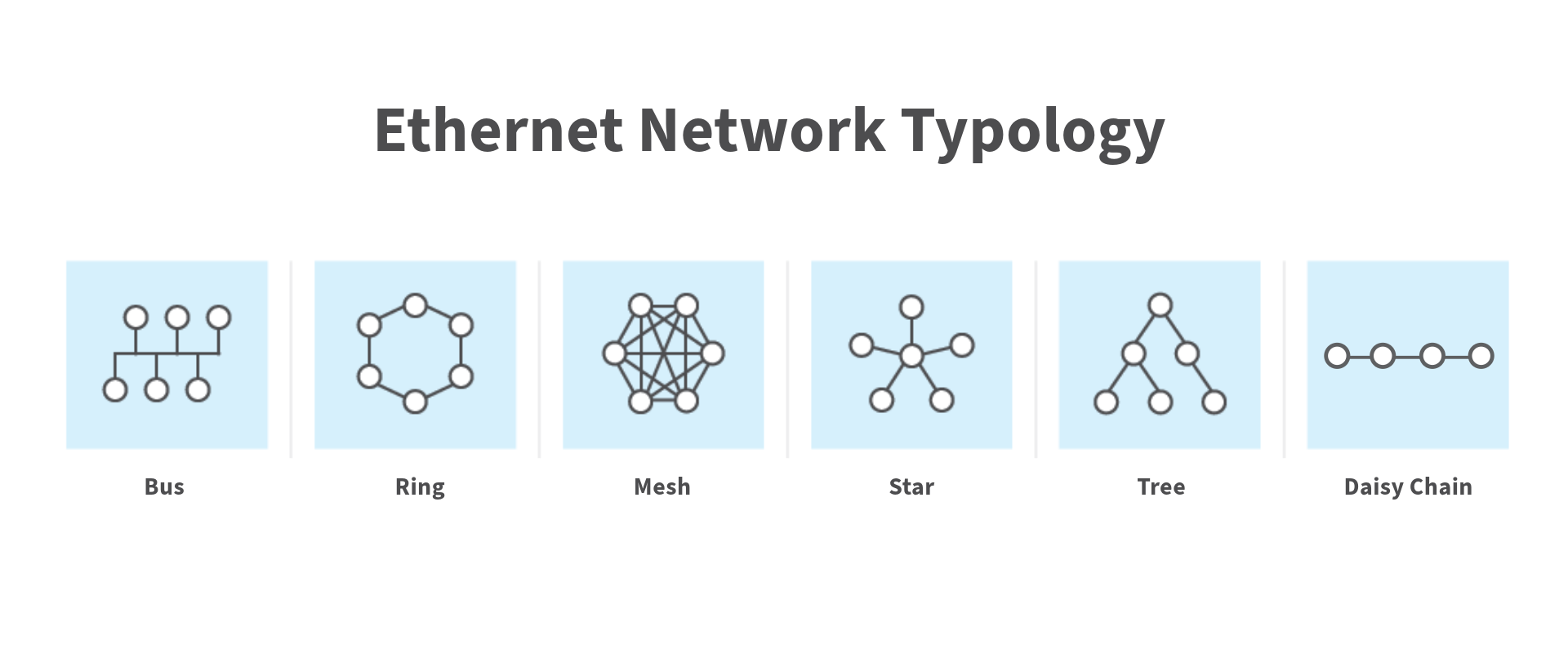
Ethernet Network Topologies
1. Star Topology
- Description: In a star topology, each device (node) on the network is connected to a central device (such as a switch or hub). All data communication passes through the central hub.
- Pros:
- Easy to manage and troubleshoot due to the central point of control.
- If one cable fails, only the connected device is affected, not the entire network.
- High performance as each device has a dedicated connection.
- Cons:
- If the central hub fails, the entire network goes down.
- Requires more cable than some other topologies.
2. Bus Topology
- Description: In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a single central cable, known as the bus or backbone.
- Pros:
- Simple and cost-effective for small networks.
- Requires less cable than star topology.
- Cons:
- If the central cable fails, the entire network is affected.
- Performance decreases as more devices are added due to collisions and traffic.
3. Ring Topology
- Description: In a ring topology, each device is connected to two other devices, forming a circular data path.
- Pros:
- Data packets travel in one direction, reducing collisions.
- Predictable network performance.
- Cons:
- If one device or connection fails, the entire network can be disrupted depending on hardware.
- More difficult to install and configure.
4. Daisy Chain Topology
- Description: In a daisy chain topology, each device is connected in a series to the next device. It can be either linear or ring.
- Pros:
- Simple to connect and extend.
- Requires less cable than star topology.
- Cons:
- If one device or connection fails, it can affect the entire network.
- Difficult to manage and troubleshoot as network grows.
5. Mesh Topology
- Description: In a mesh topology, each device is connected to every other device on the network, creating a highly redundant and fault-tolerant network.
- Pros:
- High reliability and redundancy.
- Each connection can carry its own data load, providing high performance.
- Cons:
- Very expensive and complex to install and manage.
- Requires a large amount of cable and network interfaces.
- Maximum Run Length: Typically follows Ethernet standards, but can vary widely depending on the specific implementation and devices used.
- More common in wireless networks
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
- Description: RSTP is an evolution of the original Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) designed to prevent network loops in Ethernet networks by dynamically managing the topology.
- Pros:
- Rapid convergence compared to STP, usually within a few seconds.
- Backward compatibility with legacy STP.
- Improves network resiliency and efficiency.
- Cons:
- More complex to configure than STP.
- Requires compatible network devices.
- Typical Use Cases: Used in larger, redundant network topologies to ensure loop-free, reliable connections, especially in enterprise environments.
Maximum Run Lengths for Common Ethernet Types
- 10BASE-T: Up to 328 feet over twisted-pair cabling (Cat3 or higher).
- 100BASE-TX: Up to 328 feet over twisted-pair cabling (Cat5 or higher).
- 1000BASE-T: Up to 328 feet over twisted-pair cabling (Cat5e or higher).
- 10GBASE-T: Up to 328 feet over twisted-pair cabling (Cat6a or higher).
- 10BASE2 (Thinnet): Up to 607 feet over coaxial cable.
- 10BASE5 (Thicknet): Up to 1640 feet over coaxial cable.
- 100BASE-FX: Up to 1.24 miles over multimode fiber.
- 1000BASE-SX: Up to 1804 feet over multimode fiber.
- 1000BASE-LX: Up to 3.1 miles over single-mode fiber.
Conclusion
When designing or maintaining a OT network, choosing the right topology and understanding the constraints and benefits of each type is crucial. Daisy and Ring topologies are recommended in modern OT networks due to their reliability, relative simplicity, and lower cost while more complex topologies like mesh are reserved for scenarios requiring high redundancy and performance. Understanding protocols like RSTP is essential for ensuring efficient and loop-free network operations in larger and more complex setups.Tags
bas
ot
bas network
control panels
network configuration
port security
network control
smart buildings
energy management
building automation
ethernet based
bas network guidelines
tosibox
managed switches
distech
optimizer
commander
johnson controls
eclypse
network
security
cyber
iot
ul508a
industrial solutions
engineering solutions
panel assembly
custom control panels
commercial panels
gas regulator sizing
gas safety
inlet pressure
outlet pressure
flow rate
natural gas
propane regulators
subnet
it
managed ip switch
vlan setup
quality of service
qos
spanning tree protocol
stp
routing configuration
network management
lldp setup
energy efficiency ethernet
managed network switch benefits
ot network
energy savings
building solutions
connected power
building management
bms
transformers
din rail transformer
functional devices
transformer in a box
ai in real estate
cybersecurity
data integration
realcomm ibcon
sustainability
JCI
jci
sensors
controllers
interfaces
Posts
2025
January
2024
JCI CCT Installation & Upgrade Guide
[01/31/25 09:05 AM]
Blog | $1.6 Billion Cyber Attack
[01/30/25 08:48 AM]
Blog | Cybersecurity for Building Automation
[01/27/25 09:55 AM]
Atrius Facilities: Simplify Project Management with Organize
[01/07/25 11:24 AM]
Simplifying Niagara Framework® Management
[01/03/25 03:21 PM]
November
2023
Building Automation in 2024
[11/06/24 12:46 PM]
UL508A Control Panels: Engineered Solutions
[11/04/24 09:23 AM]
October
September
Preventative Maintenance for York Chillers: Why It Matters
[09/24/24 09:42 AM]
Maximize Field Efficiency with the Connected Workflow Application (CWa)
[09/18/24 11:35 AM]
Tosibox: Simplifying Secure Connectivity for Building Automation
[09/18/24 10:35 AM]
August
Mastering Subnetting: How to Create a Secure and Efficient Subnet
[08/27/24 02:42 PM]
Comprehensive Guide to Setting Up a Managed IP Switch
[08/26/24 03:02 PM]
Why use a managed switch on an OT network?
[08/21/24 03:37 PM]
Connected Power: Energy Waste Solution
[08/14/24 10:57 AM]
Simplified Transformer Installation
[08/12/24 09:58 AM]
July
Realcomm IBCON 2024 Takeaways
[07/30/24 08:23 AM]
Ethernet based Network Types found in OT networks
[07/26/24 11:24 AM]
Ethernet based BAS Network Guidelines
[07/26/24 09:41 AM]
Benefits of Building Automation Systems
[07/05/24 09:01 AM]
June
July 4th | Independence Day Closure
[06/28/24 09:38 AM]
July 2024 N4 Certification Class
[06/28/24 09:25 AM]
Our Suppliers are Award Winners
[06/13/24 10:46 AM]
May
Essential HVAC Sensors for Improving IAQ and Building Efficiency
[05/23/24 08:52 AM]
Distech Controls Highlight
[05/22/24 08:46 AM]
Memorial Day Closure
[05/21/24 12:09 PM]
April
School HVAC and BAS Updates
[04/22/24 09:55 AM]
Update Your Tosibox Lock 100
[04/17/24 09:58 AM]
Create Your Own Quote Tool
[04/17/24 08:58 AM]
Tosibox Remote Connectivity
[04/04/24 09:12 AM]
Building Automation and Internet of Things (IoT) Unite
[04/03/24 08:35 AM]
March
Belimo Retrofit: HVAC Solutions
[03/15/24 04:19 PM]
May 2024 N4 Certification Class
[03/14/24 10:39 AM]
Tosibox Hub: Seamless Connectivity
[03/12/24 10:32 AM]
Spyder 7 & Optimizer Unitary Technical Training
[03/04/24 03:37 PM]
February
Explore the Features of Stromquist.com
[02/29/24 08:19 AM]
JACE 9000 vs 8000: Key Differences
[02/02/24 10:54 AM]
HVAC Trends in 2024
[02/01/24 10:02 AM]
January
TC300 Commercial Thermostat
[01/29/24 04:17 PM]
Seamless Building Automation: ILC 2050 BI
[01/24/24 01:31 PM]
TC500A-N Commercial Thermostat
[01/23/24 11:35 AM]
OT Security - Eliminating Threats
[01/23/24 10:21 AM]
2024 N4 Certification Class Schedule
[01/11/24 03:14 PM]
Honeywell End of Life Dates
[01/10/24 09:38 AM]
JACE 9000 Controller for Niagara 4
[01/10/24 09:08 AM]
Globe Valves vs Ball Valves
[01/10/24 12:00 AM]
December
November
2022
Christmas Hours - Stromquist Closure
[11/30/23 10:28 AM]
Distech Supply Chain Issues
[11/21/23 09:51 AM]
December 2023 N4 Certification Class
[11/10/23 09:37 AM]
October
Gas Monitoring Made Easy with Belimo
[10/19/23 08:44 AM]
Enhancing Fire Safety: Belimo's Solutions
[10/18/23 10:07 AM]
License Visibility Change
[10/06/23 03:14 PM]
Future of Building Automation Controls
[10/03/23 03:33 PM]
September
VFDs with Bypass Are Here
[09/27/23 07:55 AM]
Honeywell Optimizer Building Controllers
[09/18/23 02:04 PM]
Need Gas Detection Help? Stromquist Can help
[09/12/23 11:13 AM]
Enjoy Retirement Bill Jones
[09/11/23 02:54 PM]
Price Increase for Distech Controls
[09/11/23 01:04 PM]
Your Source for York
[09/08/23 08:54 AM]
August
Verasys | Commercial Control
[08/08/23 03:54 PM]
KMC Counter Day | Orlando, FL
[08/08/23 01:55 PM]
Wireless MS/TP Converter - New MAP Gateway
[08/04/23 03:00 PM]
July
What is a Relay? How do Relays Work?
[07/27/23 09:49 AM]
Tosibox Platform | OT Network Solutions
[07/24/23 11:30 AM]
The RIB® Trifecta
[07/20/23 04:00 PM]
August 2023 | N4 Certification Class
[07/20/23 10:44 AM]
4 Things to Know About Current Sensors
[07/10/23 03:18 PM]
How to Properly Install Butterfly Valves
[07/06/23 11:01 AM]
June
Common Abbreviations | Belimo
[06/21/23 09:05 AM]
Stromquist Regulator Webinar
[06/19/23 10:46 AM]
Gas Sensor Mounting Heights | ACI
[06/01/23 09:01 AM]
May
SMART BUILDING INTEGRATOR SUMMIT (SBIS)
[05/24/23 10:31 AM]
Honeywell VFD Lunch & Learn Certification
[05/24/23 09:44 AM]
Honeywell Flame Safeguard Training
[05/24/23 09:44 AM]
VFD Supply Chain Update
[05/22/23 12:56 PM]
Versatile RIB Relays
[05/17/23 08:51 AM]
JCI Solutions Navigator
[05/08/23 09:54 AM]
New Honeywell Smart VFDs
[05/02/23 01:21 PM]
New FX 3D Graphics
[05/02/23 10:33 AM]
April
What's New with Facility Explorer
[04/26/23 09:42 AM]
Industry Leading CO2 and Temperature Sensors
[04/19/23 09:39 AM]
What is CV, & How to Calculate it?
[04/19/23 09:12 AM]
March
December
Stromquist & Company | Easter Jours
[12/12/22 12:00 AM]
Stromquist & Company | 2022 Holiday Hours
[12/12/22 12:00 AM]
November
October
Engineered Solutions | Panel Shop
[10/26/22 10:45 AM]
Engineered Solutions | CCP Panels
[10/11/22 10:45 AM]
Engineered Solutions | Fuel Trains
[10/06/22 10:45 AM]
September
Engineered Solutions
[09/30/22 04:22 PM]
Atlanta Fast Lane
[09/22/22 10:28 AM]
Stromquist Website Updates
[09/13/22 10:15 AM]
DC2500/3200 are Obsolete
[09/07/22 02:54 PM]
Stromquist Selection Guides
[09/07/22 02:54 PM]
August
Honeywell Mod Motor Identification
[08/26/22 09:39 AM]
Variable Frequency Drive Update
[08/23/22 01:57 PM]
Apogee TEC Sensors
[08/23/22 01:57 PM]
ASCO™ Series 158 and 159
[08/23/22 01:57 PM]
The Importance of Relief Valves
[08/18/22 03:24 PM]
Testing a M91XX Mod Motor
[08/16/22 03:15 PM]
Ohms Law Explained
[08/08/22 03:07 PM]
Identifying Honeywell Parts
[08/04/22 03:16 PM]
July

